Deforming arthrosis (osteoarthritis) is a progressive pathology that leads to dystrophy and degeneration of the articular surface and damage to the cartilage, resulting in complete destruction of the joint area.
Typically, deformed arthrosis is detected in old age and old age, in the presence of corresponding factors and diseases, it is often detected during examination, but does not manifest itself clinically.
Forming arthrosis is the most frequent and widespread joint pathology. It occurs in 70% of all joint diseases.
Cause
The exact cause of deformed arthrosis has not been elucidated, but several factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of its development. First of all, this is a general aging of the body and dystrophic phenomena in tissues, cartilage changes and joint capsules.
Factors that influence the development of osteoarthritis can be divided into:
- external - this includes excessive joint load (e. g. , due to weight lifting), permanent injuries, occupational influences, joint hypothermia,
- internal - this is a hereditary influence with stretching of ligaments and joint relaxation, ovarian dysfunction and climacteric changes in women, vascular accidents, impaired blood circulation to cartilage tissue, obesity.
Damaging arthrosis, as one of the symptoms, can occur with alcoholism or myxedema, acromegaly or with hormone treatment, with congenital dislocation of the hip, Marfan syndrome (hereditary disease characterized by excessive joint movement and elongation of tubular bone). joint spasm)
Stage of development
In the development of deformed arthrosis, there are several successive stages that alternate:
- reduces the freshness of cartilage, which causes thinning and drying,
- formation of defects and cracks in the cartilage,
- destruction of cartilage with simultaneous sharp narrowing of the articular space,
- loss of cartilage from the edges of the bone,
- compaction of the ends of the bones, which are left without the surface of the cartilage,
- joint disorders with dislocations, fractures and limb dysfunction.
Symptoms of deformed arthrosis
First of all, the main manifestations of deformed arthrosis are
- pain in the joints, worse after exercise or at night,
- individual joints are affected,
- the affected joints are asymmetric,
- at the same time, there is no general manifestation of joint damage,
- no fever
- no strong joint redness,
- no change in analysis.
This process often occurs in the ankle, knee, hip or interphalangeal joints.
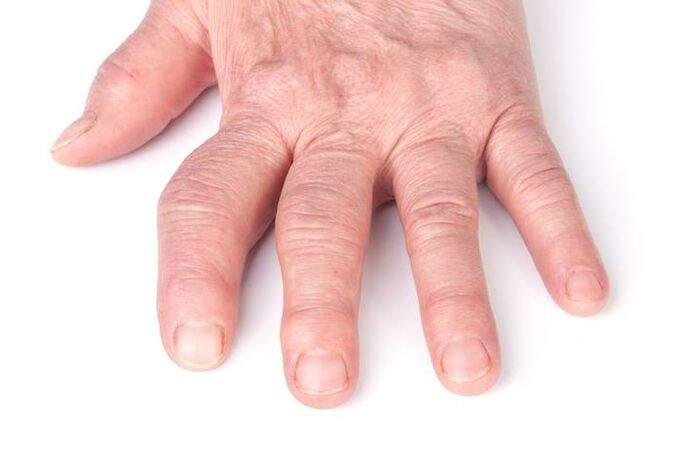

If the disease progresses to the point of cartilage destruction, painful joint blockage occurs, while walking, severe pain appears, which does not let the foot move and makes it stop. This is caused by pieces of cartilage or small bone fragments (articular "rats") entering the joint cavity.
In the joint area of the phalanges, nodular, very hard formations appear, while the joints are not too deformed, the muscles do not atrophy, and there is no ankylosis (joint inability).
Inside the joint, while moving, cracks are heard due to the uneven friction of the surfaces with each other.
Pain and limited movement can cause contractions (muscle contractions), which shorten the legs or arms.
Defective arthritis in manifestations is similar to various forms of arthritis, first of all it must be distinguished from rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnostics
There are no typical criteria for the diagnosis of deformed arthrosis; it can only be recognized from the outside by nodules on the phalanx of the finger. Osteoarthritis is suspected when:
- special joint damage,
- the development of long-term disease over many years,
- elderly patients.
The basis of the diagnosis is X-ray data that appear even before the period of clinical manifestations and pain syndromes.
There is narrowing of the joint space, changes with flattening and deformation of the joint surface, instability in the joint area with dislocation and subluxation, marginal bone growth, osteosclerosis (increase in excessive bone density) can be seen.
As the process progresses, the spine and bruises are exposed, the joint space can become wedge -shaped.
The study was complemented by arthroscopy, a blood test with no signs of inflammation.
Studies on periarticular fluid need to be done.
Treatment of deformed arthrosis
The treatment is performed by traumatologists and orthopedists.
Methods for the treatment of deformed arthrosis depend on the degree of joint involvement in the process, as well as on the lesion and the presence of pain.
First of all, conservative therapy is used.
- reduce pressure on the joints,
- weight reduction,
- use of metabolites - aloe vera or vitreous course intramuscularly in the course,
- use cartilage recovery stimulants in intramuscular injections in the course.
Completing treatment:
- use of quinolone drugs,
- anti-inflammatory therapy.
If there is inflammation in the joint, hormonal indications in the joint are indicated.
Complex massage, physiotherapeutic effects, mud therapy, thermal effects are also used. Useful spa treatments.
In further cases, surgical treatment helps - arthroplasty of the joints. In the future, joint disassembly, weight loss, walking with support on crutches or crutches, physiotherapy exercises are indicated.
Prediction
Forming arthrosis without the necessary treatment has a slow but continuous process. Leads to significant joint deformities and dysfunction, movement disorders. Therefore, when the first signs of osteoarthritis appear, active therapy is indicated, lasting for 1-2 months.



































